Shielding gas used for stainless steel welding wire
Stainless steel welding wire is widely used in various industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and aesthetic appeal. When welding stainless steel wire, it is crucial to choose the right shielding gas to ensure a successful and high-quality weld.
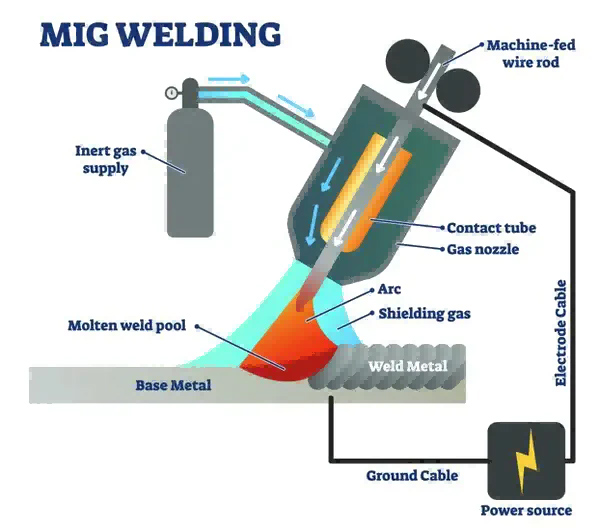
The primary purpose of shielding gas is to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. These gases can react with the molten metal, leading to defects like porosity, excessive oxidation, and reduced mechanical properties.
Argon is the most commonly used shielding gas for stainless steel welding wire. It is an inert gas that effectively displaces oxygen and provides a stable arc. Argon shields the weld pool from atmospheric gases, preventing oxidation and ensuring a clean weld. It also helps to minimize spatter and improve overall weld quality.
In some cases, a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide (CO2) is used as a shielding gas for stainless steel welding wire. This blend offers a good balance of protection and cost-effectiveness. The CO2 content in the mixture helps to stabilize the arc and improve penetration, while argon provides the necessary shielding.
The choice of shielding gas depends on various factors, including the type of stainless steel being welded, the desired weld characteristics, and the welding process used. For example, when welding austenitic stainless steel, pure argon is often preferred due to its ability to prevent the formation of chromium carbides, which can reduce corrosion resistance.

