Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding – Process and Applications
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a popular welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. This process is known for its high quality welds and precise control over the welding parameters.
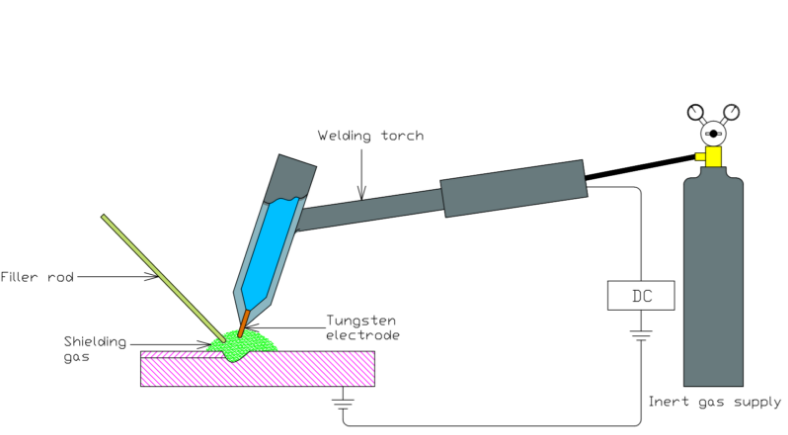
The TIG welding process involves creating an electric arc between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece, which melts the base metals and forms a weld pool. A shielding gas, typically argon or helium, is used to protect the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination. The welder can control the heat input, arc length, and welding speed to produce a high-quality weld with minimal spatter and distortion.
In conclusion, Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding is a versatile welding process that offers high-quality welds and precise control over welding parameters. Its applications are diverse, making it a popular choice in various industries.

